|
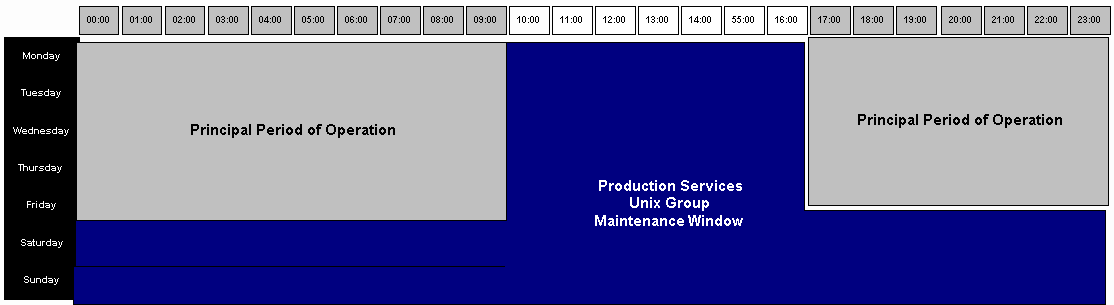
The <APPLICATION> availability and maintenance windows are shown in the following diagram. The Production Services Change Control process will be used for planned maintenance. Associated parties will be notified of maintenance per the procedures laid out in this document. |

|
The following table provides availability goals for the <APPLICATION>. These goals will be reviewed every four weeks for a three month period to determine if they can be firmly established. If any of the goals listed in the table cannot be reliably established, the provider will renegotiate a new goal with <BUSINESS UNIT>. |
|
Provider |
Hours @ 100% |
Goal (Percent) |
Hours Unplanned Downtime/Year |
|
Unix Group |
4940 |
99% |
49.4 |
|
Mainframe Group |
4940 |
N/ANote 1 |
N/A Note 1 |
|
Network Group |
4940 |
99% |
49.4 |
Note 1 – the Mainframe Group does not provide services during the Principal Period of Operations. It does, however, provide support for critical transactions that impact system functionality during the Principal Period of Operations.
|
The aggregate availability is: 98.01 %, which equals 98.3 aggregate hours of unplanned downtime per year. These numbers are derived from the following formula: UG x NG Where UG = the Unix Group goal of .99 and NG = the Network Group goal of .99 Aggregate hours of unplanned downtime is computed by multiplying aggregate availability by 4940 hours (hours availability at 100%). and subtracting the result from 4940. |
|
The following computations were used to compute the availability goal hours @ 100% and hours of unplanned downtime per year: Principal Hours of Availability from Midnight to 10:00 AM Monday through Saturday = 60 hours (10 hours x 6 days) + Principal Hours of Availability from 17:00 to Midnight Monday through Friday = 35 hours (7 hours x 5 days) = 95 hours per week required availability. 95 hours/week x 52 weeks = 4940 hours of required availability at 100% per year. The total hours of required availability is multiplied by the goal to arrive at total hours of committed availability, which is subtracted from the number of hours at 100% to arrive at hours of unplanned downtime per year. |
|
The following are possible reasons for unplanned downtime, which is why Production Services cannot guarantee 100% of required availability:
Note: In the case of a requirement to restore a corrupted file, the cycle time to perform this task is constrained by the fact that tapes are stored off-site and cannot be retrieved in less than four hours. |
|
Although the <APPLICATION> has no interactive users, there are approximately 150 users who depend on services provided by this system. It is estimated that each user will operate at 50% efficiency if the <APPLICATION> is unavailable, which results in a loss of approximately 75 person hours for every hour of unplanned downtime. Communication procedures in the event of Unplanned Downtime are specified in Object 3 – Support. Note: The above impact assessment does not take into account intangibles such as lost opportunities, diminished goodwill or the actual costs associated with the person hour loss. These costs need to be identified by the <BUSINESS UNIT> in order to quantify the actual cost of downtime. |